What are the NFTs?
NFT stands for “non-fungible tokens”. It’s a form of a cryptographic token created on a smart contract platform, such as Ethereum. Such tokens can represent ownership of digital goods, such as art or collectibles. Kings of Leon have recently released their album as an NFT. Another case is Mike Winkelmann, a digital artist better known as “Beeple” who sold over 3,5 million dollars worth of NFT artwork over a weekend. Sounds pretty expensive for a couple of JPGs?- let’s jump into how NFTs really work and where the value is hidden.

“Guy Fawkes Night” by Beeple
Fungible vs. non-fungible
“Fungibility is the property of a good or a commodity whose individual units are essentially interchangeable, and each of its parts is indistinguishable from another part.” For example, the bill you have in your pocket can be replaced or exchanged with another one without losing any value or other properties. The same goes for cryptocurrencies that can also be fungible, meaning all the currency’s units are the same and equal.
Non-fungible tokens are the opposite. Every cryptocurrency unit or token is unique and cannot be replicated. Just like a piece of art, it’s usually created as one original copy and its price depends on factors such as its age, history, authors recognition, technique, and more. When we’re talking about collectibles, such as cards, two copies of the same collectible card can have different prices, depending on the physical condition, year of production, and other factors making it more or less unique.
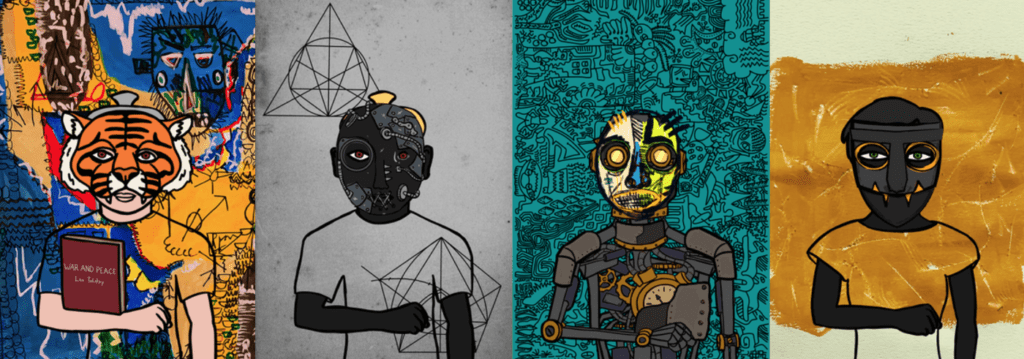
"Hashmasks" managed by Suum Cuique Labs.
NFT properties
- NFTs are unique, each one has different properties stored in the tokens metadata.
- They are provably scarce, which means there is a limited number of NFTs but they can be verified on the blockchain, hence its provability.
- Indivisible. They can’t be split into smaller parts, meaning you can’t buy a fraction of an NFT like you can buy a 0,0000001 BTC.
- Guarantee the ownership of a certain asset.
- Easily transferable
- Can be implemented on any platform supporting smart contracts
This “non-fungible” property can be used for many things, but the recent NFT hype is mostly fueled by digital art, collectibles, and games. People have figured out that a unique, digital object can have a significant monetary value in the near future so they seek an investment opportunity, but it would be wise to do some research before doing that. Skeptics say that the hype around NFTs and crypto looks similar to the “.com bubble.”
Paying money for JPEGs
Many NFTs are just digital images that you can easily save to your computer by right-clicking them, so why do people invest money in NFT art? Thanks to the files existing on the blockchain it is extremely hard to copy them entirely. The blockchain entry also tells you who created the original NFT and the blockchain will verify it. The ownership of an NFT is always assigned to a single person, but anyone can view it at any time. It’s like a forever open display of art and collectibles.
Some NFTs can serve a quite different purpose. You can purchase an NFT implemented into an online game and hope that its value will grow with time and give you that cool look and prestige in the game meanwhile. MMORPG games have a long history of pretty pricey trades. NFTs let you be sure that your valuable weapon, armor, or other cosmetic items can be never taken away from you, even by the game owners.
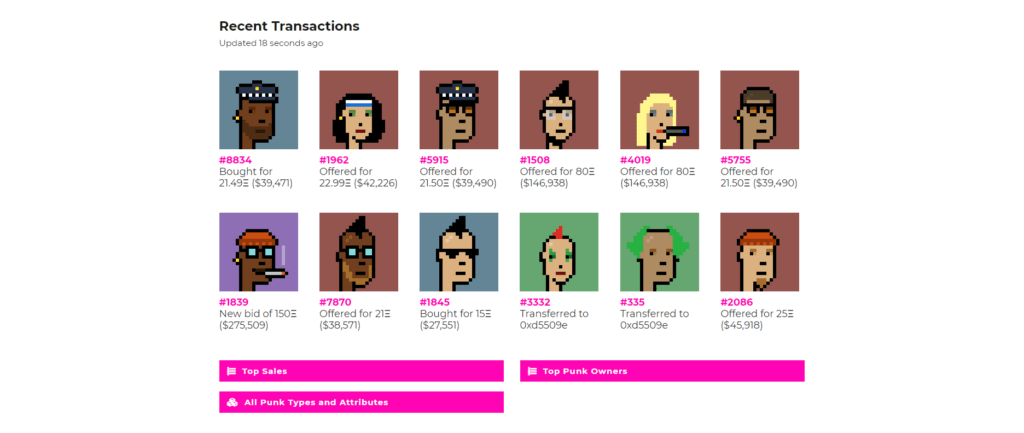
The majority of NFTs are created on Ethereum’s blockchain, which cannot be altered. No one can cancel, or recreate your ownership of an NFT. They also need no “permissions,” so anyone can create, buy, or sell an NFT without permissions. Its presence as a digital asset on the blockchain is what makes it valuable, not the file itself. NFT art series such as hashmasks, crypto punks or cryptokitties are in high demand at the moment and being traded on sites such as OpenSea or SuperRare for millions of dollars every day.
Follow us on Spotify: